Understand Multi threading
Before dive into the Thread Programming, we should know what is Thread and why should we use thread.
What is thread and Why we need Thread
Thread is a concept of C# which used to run code segment simultaneously by using multiple threads.
Kernel schedule the threads asynchronously, which makes the application execution faster and no need to wait for a code segment to execute completely.
Thread is most important when the code segment like methods are taking time and need to wait for the method to execute the application.
Switching CPU between multiple threads to execute code segments is called Context Switching.
Description
We know each application runs using a process . That process use at least one thread.
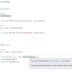
1.In the above multi-threading example we created 2 threads.
We assign the related methods to the constructor of the thread class(Highlighted).
Thread mythread1 = new Thread(method1); Thread mythread2 = new Thread(method2);
2.In the next step we define 2 methods which uses loop to display numbers as shown below.
private static void method1()
{
for (int i = 0; i <= 10; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("Method1 " + i);
}
}
private static void method2()
{
for (int j = 11; j <=20; j++)
{
Console.WriteLine( "Method2 " + j);
}
}
3.In the next step we start the thread using Start() method as shown below .
mythread1.Start(); mythread2.Start();
After the code we need to Run the application by using Run Icon available in Visual Studio or we can press Ctrl+f5.
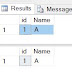
We can see the the below Output.
In The above image you can see the values are not printed in systematic order why?
The reason behind this is CPU is shared between two threads asynchronously. That is the reason why both method1() and method2() run asynchronously.
Benefits of Multi-Threading Application
So ultimately we can say each application use at least one thread by default. That is called Main thread.
We can create child thread and assign the code segment to it.
Thread use CPU Usage efficiently.
Thread use System.Threading Namespace to use the Thread class methods and Properties.
Thread Life cycle
It goes through 4 steps as shown below.
It goes through 4 steps as shown below.
- New-When Only the Instance of the thread got created.
- Running-When thread is in running state , that time Start() called.
- Blocked or Hold state- When Thread got started but that time thread is in Hold state.
- Complete or dead State- When thread ended and not run again.
 |
| Multi-Threading Life Cycle In C# |
Sample Multi-threading Program
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Thread mythread1 = new Thread(method1);
Thread mythread2 = new Thread(method2);
mythread1.Start();
mythread2.Start();
Console.ReadKey();
}
private static void method1()
{
for (int i = 0; i <= 10; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("Method1 " + i);
}
}
private static void method2()
{
for (int j = 11; j <=20; j++)
{
Console.WriteLine( "Method2 " + j);
}
}
}
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Thread mythread1 = new Thread(method1);
Thread mythread2 = new Thread(method2);
mythread1.Start();
mythread2.Start();
Console.ReadKey();
}
private static void method1()
{
for (int i = 0; i <= 10; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("Method1 " + i);
}
}
private static void method2()
{
for (int j = 11; j <=20; j++)
{
Console.WriteLine( "Method2 " + j);
}
}
}
1.In the above multi-threading example we created 2 threads.
We assign the related methods to the constructor of the thread class(Highlighted).
Thread mythread1 = new Thread(method1); Thread mythread2 = new Thread(method2);
2.In the next step we define 2 methods which uses loop to display numbers as shown below.
private static void method1()
{
for (int i = 0; i <= 10; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("Method1 " + i);
}
}
private static void method2()
{
for (int j = 11; j <=20; j++)
{
Console.WriteLine( "Method2 " + j);
}
}
3.In the next step we start the thread using Start() method as shown below .
mythread1.Start(); mythread2.Start();
After the code we need to Run the application by using Run Icon available in Visual Studio or we can press Ctrl+f5.
We can see the the below Output.
In The above image you can see the values are not printed in systematic order why?
The reason behind this is CPU is shared between two threads asynchronously. That is the reason why both method1() and method2() run asynchronously.
Benefits of Multi-Threading Application
- Faster Execution.
- Proper utilization of CPU because of Context Switching.
Demerits of Multi-Threading Application
- If code segment is not taking much time , then implementing threading makes an adverse affect on the application execution time.
- Application may fail to show expected data if we not implement threading in a proper way.
- Multi-Thread makes application more Complex , this means difficult to debug and mentain multi-threaded application.
Conclusion
- Multi-Threading Implementation should be proper in the application.
- Multi-Threading should not be used in small fast running application.
- Multi-Thread should be used in big application where the code segment took time to execute.










No comments:
Post a Comment