Thread synchronization
Thread synchronization is a technique used in threading, Which allows only one thread to access the resources for a specific time period.No other thread interrupt till current task is completed. |
| Thread Synchronization |
It uses 3 techniques.
- Monitor Or Lock
- Mutex
- Semaphore
1.Monitor Or Lock- It uses when multi-threaded application with single process.It uses Monitor class Or Lock keyword to synchronize the multi-threaded application.
It uses "System.Threading" Namespace.
We can demonstrate the lock keyword as below.
lock(object)
{
}
Lets understand with an example.
lock Example
class ThreadLock
{
public static void Main()
{
ThreadLock tl = new ThreadLock();
Thread th = new Thread(tl.ThreadRun);
Thread th1 = new Thread(tl.ThreadRun);
Thread th2 = new Thread(tl.ThreadRun);
th.Start();
th1.Start();
th2.Start();
Console.WriteLine("Completed Successfully.........");
Console.Read();
}
Random r = new Random();
public int num1;
public int num2;
public void ThreadRun()
{
for (long var1 = 0; var1 < 10000000; var1++)
{
lock (this)
{
num1 = r.Next(1, 2);
num2 = r.Next(1, 3);
int result = num1 / num2;
num1 = 0;
num2 = 0;
}
}
}
}
{
public static void Main()
{
ThreadLock tl = new ThreadLock();
Thread th = new Thread(tl.ThreadRun);
Thread th1 = new Thread(tl.ThreadRun);
Thread th2 = new Thread(tl.ThreadRun);
th.Start();
th1.Start();
th2.Start();
Console.WriteLine("Completed Successfully.........");
Console.Read();
}
Random r = new Random();
public int num1;
public int num2;
public void ThreadRun()
{
for (long var1 = 0; var1 < 10000000; var1++)
{
lock (this)
{
num1 = r.Next(1, 2);
num2 = r.Next(1, 3);
int result = num1 / num2;
num1 = 0;
num2 = 0;
}
}
}
}
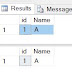
OUTPUT
 |
| Monitor-Output |
Lets Understand the above program
In Main() we created 3 threads and all the threads pointing to the same method ThreadRun().
In ThreadRun() we have a long running loop and trying to divide 2 numbers. With in the for Loop we used lock synchronization technique to synchronize the program. That means only one thread can use the resources at a time and program can run smoothly.
2. Mutex- It uses when we use multi-threaded application with single or multiple processes. It is similar to lock/Monitor. It uses Mutex class for multi-threaded application synchronization.
It use System.Threading Namespace.
It Uses 2 methods.
- WaitOne() - It allows single thread to use the resources.
- ReleaseMutex()- It release current thread and allow other thread to use the resource.
Skeleton of Mutex
Mutex mu=new Mutex();
mu.WaitOne();
mu.ReleaseMutex()
Lets Understand Mutex with a C# Program
class ThreadMutex
{
public static Mutex mut = new Mutex();
public static int iteration =3;
public static void Main()
{
Thread thread1 = new Thread(Mutex_Method);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(Mutex_Method);
Thread thread3 = new Thread(Mutex_Method);
thread1.Name = "Thread1";
thread2.Name = "Thread2";
thread3.Name = "Thread3";
thread1.Start();
thread2.Start();
thread3.Start();
Console.Read();
}
private static void Mutex_Method()
{
Console.WriteLine(Thread.CurrentThread.Name + " Started...");
mut.WaitOne();
Console.WriteLine("Currently " + Thread.CurrentThread.Name + " Entered...");
Thread.Sleep(500);
Console.WriteLine(Thread.CurrentThread.Name + " Done processing...");
mut.ReleaseMutex();
Console.WriteLine(Thread.CurrentThread.Name + " is released...");
}
}
Output
 |
| Mutex-Output |
In Main() we created 3 threads and all the threads pointing to the same method Mutex_Method().
In Mutex_Method() we use WaitOne() which signal the program to allow only one thread to use the resources.Other threads need to wait until the current thread finish it's work.
We use ReleaseMutex() which signal the program to release the current thread and allow other thread to use the resources.
3. Semaphore It is used for multi-threaded application . Unlike Monitor and Mutex it allows multiple thread based upon the value defined.
We can define Semaphore as below.
Semaphore semapr = new Semaphore(2,2);
Where value passed in the above constructor is (2,2) 1st 2 is the Initial count and other 2 is the maximum count
It use System.Threading Namespace.
It Uses 2 methods.
- WaitOne() - It allows defined number of threads to use the resources.
- Release()- It release current threads and allow other thread to use the resources.
Note-Semaphore allows multiple threads(based upon the value defined in Semaphore constructor) to use the resources at a time.
Skeleton of Semaphore
Semaphore semap=new Semaphore (2,2); //This allows 2 threads to use the resource at a time
semap.WaitOne();
semap.Release()
Lets Understand Semaphore with a C# Program
class Semaphore_Example
{
public static Semaphore semapr = new Semaphore(2,2);
public static void Main()
{
Thread thread1 = new Thread(Semaphore_Method);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(Semaphore_Method);
Thread thread3 = new Thread(Semaphore_Method);
thread1.Name = "Thread1";
thread2.Name = "Thread2";
thread3.Name = "Thread3";
thread1.Start();
thread2.Start();
thread3.Start();
Console.Read();
}
private static void Semaphore_Method()
{
Console.WriteLine(Thread.CurrentThread.Name + " Started");
semapr.WaitOne();
Console.WriteLine(Thread.CurrentThread.Name + " Entered");
Thread.Sleep(1000);
Console.WriteLine(Thread.CurrentThread.Name + " Releasing.....");
semapr.Release();
}
}
{
public static Semaphore semapr = new Semaphore(2,2);
public static void Main()
{
Thread thread1 = new Thread(Semaphore_Method);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(Semaphore_Method);
Thread thread3 = new Thread(Semaphore_Method);
thread1.Name = "Thread1";
thread2.Name = "Thread2";
thread3.Name = "Thread3";
thread1.Start();
thread2.Start();
thread3.Start();
Console.Read();
}
private static void Semaphore_Method()
{
Console.WriteLine(Thread.CurrentThread.Name + " Started");
semapr.WaitOne();
Console.WriteLine(Thread.CurrentThread.Name + " Entered");
Thread.Sleep(1000);
Console.WriteLine(Thread.CurrentThread.Name + " Releasing.....");
semapr.Release();
}
}
Output
 |
| Semaphore Output |
In Main() we created 3 threads and all the threads pointing to the same method Semaphore_Method().
In Semaphore_Method() we have implemented WaitOne() which signal the program to allow defined number of thread to use the resources.Other threads need to wait until the current thread release the resources.
We use Release() which signal the program to release the current threads and allow other threads for resources.
Things To Remember...
- Lock/Monitor used to allow one thread at a time for a single process
- Mutex is like Lock/Monitor but it allows multiple process.
- Semaphore allows multiple threads to use the resources at a time.
- Lock/Monitor has batter performance among all.
Thanks.................................