Introduction
ManualResetEvent is One of the Most important topic in C# threading.
This helps to manage Synchronize Threading with the help of Signals.
Those who wanted to learn advanced Threading, this topic is for them.
You can check AutoResetEvent for more information.
Description
ManualResetEvent basically consists of 2 parts.
Conclusion
ManualResetEvent is One of the Most important topic in C# threading.
This helps to manage Synchronize Threading with the help of Signals.
Those who wanted to learn advanced Threading, this topic is for them.
You can check AutoResetEvent for more information.
Description
ManualResetEvent basically consists of 2 parts.
- WaitOne()
- Set()
WaitOne() - Allow the thread in a halt mode
Set() - Give signal to thread to continue from where the thread stopped.
Program Skeleton
static ManualResetEvent manualreset = new ManualResetEvent(false);
public static void Main()
{
Thread thread1 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(ManualResetMethod));
thread1.Start();
manualreset.Set();
}
public static void ManualResetMethod()
{
//Write Here
manualreset.WaitOne();
//Write Here
}
Flow Chart Diagram
Lets understand the above diagram.
 |
| Manual-Reset-Event |
Lets understand the above diagram.
- As per the above diagram we need to create a thread
- Start a thread.
- Call WaitOne() several times with in the method which will make the execution Pause.
- Call the Set() which will send signal to all WaitOne() to resume the execution.
- This leads to give the complete output .
Lets Understand the above diagram with a simple program.
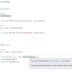
Program
class ManualResetEventExample
{
static ManualResetEvent manualreset = new ManualResetEvent(false);
public static void Main()
{
Thread thread1 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(ManualResetMethod));
thread1.Start();
Console.ReadKey();
manualreset.Set();//For manual reset only 1 "Set" required for all "WaitOne"
Console.ReadKey();
}
public static void ManualResetMethod()
{
manualreset.WaitOne();
Console.WriteLine("Thread started.....");
manualreset.WaitOne();
Console.WriteLine("Thread Ended.....");
manualreset.WaitOne();
Console.WriteLine("Thread2 Started.....");
manualreset.WaitOne();
Console.WriteLine("Thread2 Ended.....");
}
}
class ManualResetEventExample
{
static ManualResetEvent manualreset = new ManualResetEvent(false);
public static void Main()
{
Thread thread1 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(ManualResetMethod));
thread1.Start();
Console.ReadKey();
manualreset.Set();//For manual reset only 1 "Set" required for all "WaitOne"
Console.ReadKey();
}
public static void ManualResetMethod()
{
manualreset.WaitOne();
Console.WriteLine("Thread started.....");
manualreset.WaitOne();
Console.WriteLine("Thread Ended.....");
manualreset.WaitOne();
Console.WriteLine("Thread2 Started.....");
manualreset.WaitOne();
Console.WriteLine("Thread2 Ended.....");
}
}
Conclusion
- ManualResetEvent will help to Pause and Resume the thread.
- WaitOne() helps to pause the thread.
- Set() used to Resume thread.
- For each All WaitOne() one Set() is required to resume the thread unlike AutoResetEvent.