switch case or Switch statement
Switch statement is used to move the program control to a specific "Switch Case" based upon the Switch expression.
It can be used as a alternative to IF-ELSE.
Below is the skeleton for the Switch case .
{
case value-1:
Statement
break;
case value-2:
Statement
break;
case value-3:
Statement
break;
default:
Statement
break;
}
In the above , Expression can be any non null value . based upon the value of "Expression" the statement will be executed.
Lets Understand with a flow chart .
 |
| Flow Chart for Switch Statement,switch case |
In the Above chart Enter a value to the switch statement Say "Age". Then switch Case will compare the "Age" value to the Case statement value and Print the statement.
Before Writing the program lets understand the algorithm.
Step 1. Start
Step 2. Read Age
Step 3. Case 1:
print "Your age is 1"
Step 4. Case 2:
print "Your age is 2"
Step 5. Case 3:
print "Your age is 3"
Step 6. Default:
print "You are not a child"
Step 7. End
Lets Convert above chart and Algorithm to a Program and check the output.
using System;
namespace Console-Application
{
class Switch-Check
{
public static void Main()
{
int iAge = 0;
Console.WriteLine("Enter a number....");
iAge = Convert.ToInt16(Console.ReadLine());
switch (iAge)
{
case 1:
Console.WriteLine("Your Age is " + iAge);
break;
case 2:
Console.WriteLine("Your Age is " + iAge);
break;
case 3:
Console.WriteLine("Your Age is " + iAge);
break;
default:
Console.WriteLine("Your are not a child");
break;
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
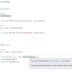
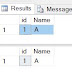
Output
See above output after running the above program in the visual studio.
In first output our entered value matches the Case statement so it printed the statement.
In second output our entered value did not matches the Case statement so it printed the statement which is Default one.
In second output our entered value did not matches the Case statement so it printed the statement which is Default one.
Few Points Need to Know about switch statement
1.It checks only the match "Case" equal to switch statement value and show the output rather than check each "Switch Case" unlike if-else.
2.It uses Jump table which makes Switch statement faster over if-else.
3.When conditions becomes very long in a program then we should prefer Switch over if-else.